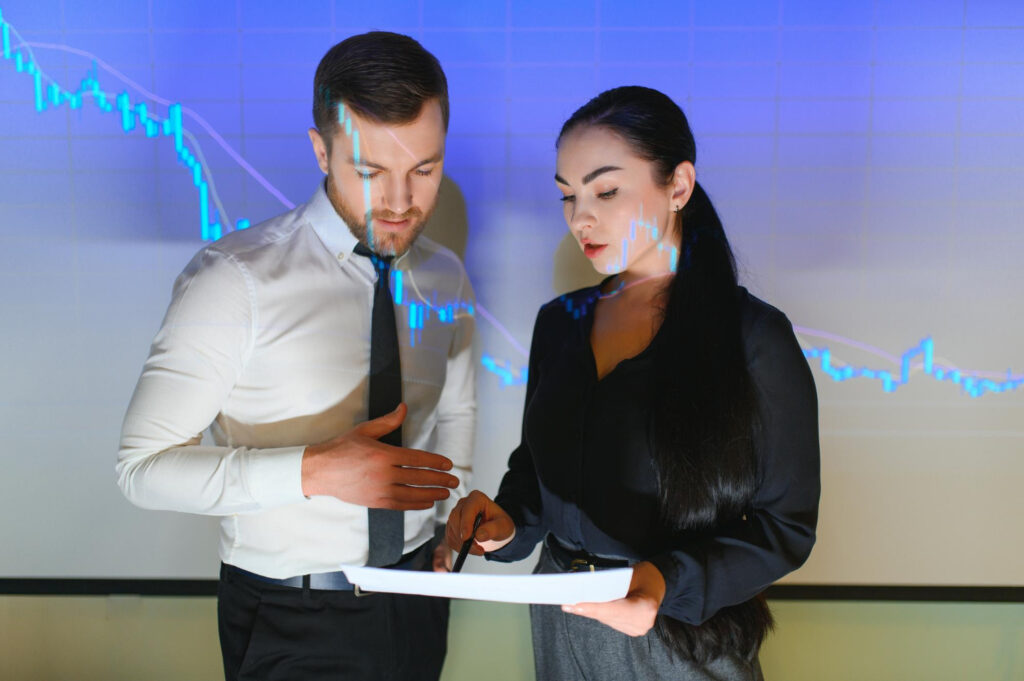
Importance of Sustainable Investing and ESG Criteria in Financial Analysis
Sustainable investing, which incorporates Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) criteria, has become a key factor in modern financial analysis. Making educated investment decisions requires an awareness of ESG criteria, since stakeholders and investors want more openness and ethical standards. In addition to addressing moral issues, sustainable investing looks for opportunities that support steady, long-term financial growth [1].
Investing in the Future: The Rise of ESG Criteria!
In recent years, the slogan “investing in the future” has gained traction as ESG criteria have taken center stage in financial markets. The emergence of ESG criteria demonstrates a rising realization that sustainable and ethical investment practices are more than just a trend, but an essential component of long-term financial success. Companies and financial experts alike are embracing this transition, incorporating ESG aspects into more educated, ethical and successful investing strategies [2].
Understanding ESG Criteria
Explanation of Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Criteria
ESG criteria assess an organization’s efficacy and influence across three important domains [3]:
- Environmental: This focuses on the actions taken by a business to reduce its influence on the environment, such as resource conservation, waste management and energy use.
- Social: This evaluates a business’s labor practices, community involvement and labor interactions with suppliers, consumers, as well as workers in the areas in which it works.
- Governance: This entails assessing the structures and procedures of a company’s governance, including executive compensation, diversity on the board and transparency.
Importance of ESG Factors in Investment Decision-Making
Identifying risks and possibilities that standard financial analysis might miss is made easier by incorporating ESG considerations into investment decision-making. Since businesses with robust ESG policies are frequently better equipped to handle legislative changes, market upheavals and reputational concerns, ESG criteria can have an impact on long-term financial performance. ESG considerations are becoming more and more important to investors in terms of sustainable and ethical investing [4].
Examples of ESG Metrics and Benchmarks Used by Financial Analysts
Financial analysts use a variety of ESG criteria and standards to evaluate corporate performance:
- Carbon footprint: A measure of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Social Impact Ratings: Assesses employee happiness and community engagement.
- Governance Scores: Evaluates board diversity and CEO compensation schemes.
Common benchmarks include the MSCI ESG Ratings and the Sustainalytics ESG Risk Ratings, which give standardized assessments of a company’s ESG performance.
Integration of ESG into Investment Strategies
How Financial Analysts Incorporate ESG Considerations into Portfolio Management
By assessing businesses according to their ESG performance and using these insights to investment decisions, financial analysts incorporate ESG factors into portfolio management. This entails applying ESG standards to prospective investments, redistributing assets to support businesses with robust ESG policies and regularly assessing the ESG performance of holdings in the portfolio. Aligning investments with both financial and sustainability goals is the aim.
Case Studies of Successful Sustainable Investment Strategies
- BlackRock’s Sustainable Investing Strategy: BlackRock, a global asset management giant, has incorporated environmental, social and governance (ESG) standards into its investment approach, emphasizing businesses that have strong sustainability policies. This strategy has produced a number of ESG-themed funds, proving that sound financial performance can coexist with sustainable investment practices [5].
- The Calvert Impact Capital Approach: By funding initiatives that provide both financial returns, as well as positive social and environmental effects, Calvert Impact Capital has effectively carried out a sustainable investment approach. Their methodology places equal emphasis on effect and profitability [6].
Impact of ESG Integration on Investment Returns and Risk Management
Integrating ESG criteria can boost investment returns by finding companies with sustainable practices, which may result in decreased long-term risks and improved performance. ESG integration aids in controlling risks associated with environmental restrictions, social challenges and governance failures. According to studies, organizations with high ESG performance tend to have reduced volatility and better long-term financial results.
ESG Data and Analysis Tools
Sources of ESG Data and Tools for Analysis
ESG data sources include specialized suppliers such as MSCI, Sustainalytics and Bloomberg, which give complete information about firms’ environmental, social and governance performance. These platforms collect and analyze data from corporate reports, regulatory filings and other public sources, enabling financial analysts to properly evaluate ESG factors [7].
Technologies Supporting ESG Data Collection and Reporting
Advances in technology have transformed ESG data collecting and reporting. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are useful tools for analyzing large volumes of ESG data, recognizing trends and projecting future performance. Furthermore, blockchain technology is developing as a method for increasing transparency and accuracy in ESG reporting by creating a tamper-proof record of data [8].
Role of Financial Analysts in Interpreting and Leveraging ESG Data
Financial analysts play an important role in evaluating and incorporating ESG data into investment analyses. They examine the significance of ESG measurements, the reliability of data sources and apply insights to guide investment decisions. To improve their research and recommendations, analysts must keep up with developing ESG trends and technology.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
Overview of Regulations and Standards Governing ESG Investing
The regulatory environment for ESG investing is continuously expanding. Key legislation includes the European Union’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), which mandates financial firms to explain how they incorporate ESG factors into their investment operations. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is increasingly focused on ESG disclosures, requiring corporations to publish more specific information about their environmental and social consequences [9] [10].
Compliance Requirements for Financial Institutions and Asset Managers
Financial institutions and asset managers must follow a variety of standards requiring openness and responsibility in ESG investment. Compliance entails meeting disclosure requirements, creating strong ESG integration processes and ensuring that investment products fulfill regulatory standards. This entails creating thorough ESG rules, performing frequent audits and giving detailed reports to regulators and stakeholders.
Strategies for Financial Analysts to Navigate Regulatory Challenges in ESG Investing
Financial analysts can overcome regulatory hurdles by staying up to date on current and upcoming rules, continuing their education on ESG standards and communicating with compliance professionals. Implementing best practices in ESG reporting and ensuring that investment plans meet regulatory criteria are also critical. Analysts could also use technology and data analytics to simplify compliance procedures and increase transparency.
Spotlight on Financial Analysts
The Evolving Role of Financial Analysts in Sustainable Investing
Financial analysts now play a larger role in sustainable investing than traditional financial analysis. Analysts are now responsible for examining ESG aspects in order to present a more complete picture of investment opportunities and risks. They must include ESG factors into financial models, interact with firms about their sustainability policies and help build sustainable investing strategies [11].
Skills and Expertise Required to Assess and Integrate ESG Criteria
To properly examine and integrate ESG criteria, financial analysts require a combination of expertise.
- ESG Knowledge: An understanding of ESG measures, standards and reporting frameworks.
- Analytical Skills: The ability to evaluate complicated ESG data and use it into financial analyses.
- Communication Skills: Ability to deliver ESG insights to stakeholders and clients.
- Regulatory Awareness: Understanding of the relevant regulations and compliance standards.
Continual education and certification in ESG-related areas can further enhance an analyst’s expertise and credibility.
Tips for Aspiring Financial Analysts to Build a Career in Sustainable Finance
Aspiring financial analysts can advance their careers in sustainable finance by [12]:
- Pursuing Relevant Education: Take ESG and sustainable finance courses or get certified.
- Gaining Experience: Look for internships or positions that focus on ESG analysis or sustainable investing.
- Networking: Connect with industry professionals to remain up to date on trends and opportunities.
- Keeping Up: Stay current on the latest advancements in ESG rules, tools and best practices.
Conclusion
ESG-driven sustainable investing is changing the financial landscape by helping investors and corporations alike match financial objectives with social and environmental concerns. Leading this change are financial analysts, who use their knowledge to evaluate risks, spot opportunities and include ESG considerations into investment plans. The increasing focus on ESG performance highlights the importance of financial analysts in navigating this rapidly changing industry and reflects a broader commitment to long-term sustainability and responsible investment practices.
As the legal landscape and technological innovations continue to shape ESG investing, financial analysts must stay updated and adjust their expertise accordingly. Analysts that master ESG measures, use advanced data analysis techniques and understand regulatory requirements can provide useful insights that support sustainable and lucrative investment decisions. The incorporation of ESG criteria not only improves investment strategies, but also helps to create a more responsible and robust financial system, making financial analysts’ roles more important than ever.
References:
Morgan Stanley: Sustainable Investing: https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/sustainable-investing
Harvard Business Review: The Rise of ESG: https://hbr.org/2021/02/the-rise-of-esg
MSCI ESG Ratings: https://www.msci.com/our-solutions/esg-investing/esg-ratings
Sustainalytics ESG Risk Ratings: https://www.sustainalytics.com/esg-risk-ratings
BlackRock’s Sustainable Investing Approach: https://www.blackrock.com/us/individual/insights/sustainable-investing
Calvert Impact Capital’s Strategy: https://www.calvertimpactcapital.org/our-strategy
MSCI ESG Data: https://www.msci.com/our-solutions/esg-investing/esg-data
Bloomberg ESG Data Solutions: https://www.bloomberg.com/professional/solution/esg-data/
European Union SFDR Overview: https://ec.europa.eu/info/business-economy-euro/banking-and-finance/sustainable-finance_en
SEC ESG Disclosures: https://www.sec.gov/esg
CFA Institute: ESG and Sustainable Finance: https://www.cfainstitute.org/en/research/esg-investing
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) – Careers in ESG: https://www.globalreporting.org/information/careers/
Are You Looking to Hire a Proven Financial Analyst?
Helping companies discover the perfect talent for their needs. Finding the right individuals to drive your success is what we excel at.