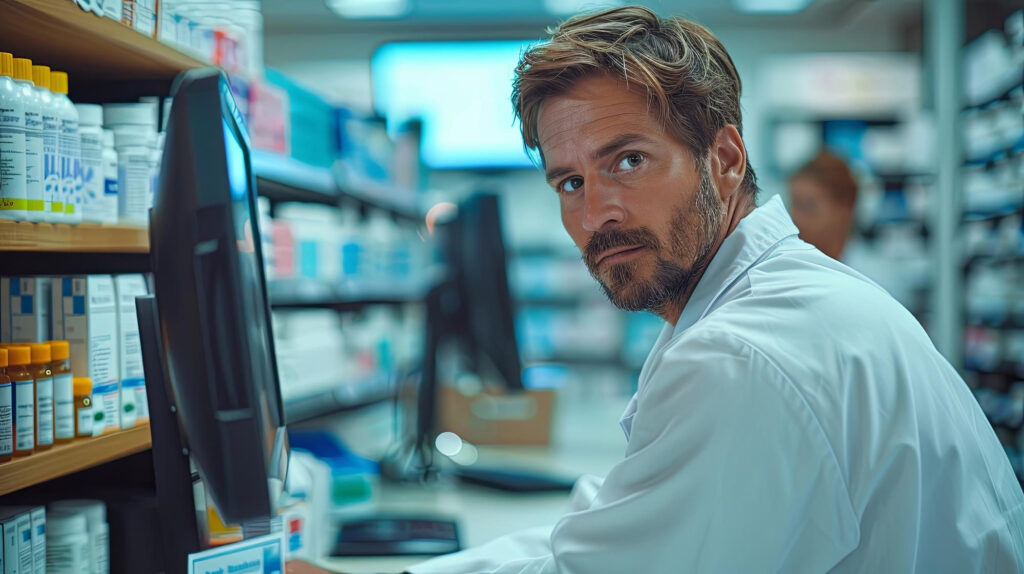
Pharmacy IT specialists have become vital to the current healthcare system because they can effectively combine state-of-the-art technology with pharmaceutical knowledge to improve patient care. By using advanced software tools, they assist clinical judgments, expedite pharmacy processes and ensure the correctness of drug records. Pharmacy IT is an essential part of modern healthcare because of this special combination of pharmacy and information technology, which not only streamlines workflow but also dramatically improves patient safety.
Overview of the diverse roles within pharmacy IT
Pharmacy IT specialists work in a variety of capacities, including clinical informaticists, software developers and systems analysts. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects an 8% increase in employment of health information positions between 2019 and 2029. This increase demonstrates the growing need for professionals with experience creating pharmaceutical management systems and overseeing electronic health data.
Pharmacy Informaticist
A pharmacy informaticist is a specialist in the medical field who combines information technology with clinical pharmacy practice to enhance drug management as well as patient outcomes. They create, put into place and manage systems for:
- EHRs, or electronic health records
- Physician Order Entry by Computer (CPOE)
- Systems for Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
Important data:
- Using informatics interventions, 80% of healthcare organizations reported increased patient safety and decreased prescription mistakes, according to the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS).
- Pharmacy informaticists improve the precision, effectiveness and security of medicine administration in healthcare settings by utilizing data analytics along with
Implementation Specialist
In pharmacy IT, an implementation specialist is a professional who manages the effective deployment and integration of technological solutions in healthcare settings. They have to coordinate with stakeholders, set up processes, give training and make sure that transfers go well. Important duties include:
- Managing Projects for Implementation
- Setting Up Technical Solutions
- Offering Guidance and Assistance
Healthcare organizations witnessed a 45% decrease in medication mistakes after implementing electronic drug administration records (eMARs) under the direction of implementation professionals, according to research by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS).
Through the successful deployment of pharmacy IT systems, Implementation Specialists contribute significantly to improving patient safety and workflow efficiency with their knowledge.
Systems Analyst
In pharmacy IT, a systems analyst is in charge of assessing, creating and putting into practice technological solutions that satisfy the demands of healthcare institutions. Their functions entail the following:
- Examining the Needs of the System
- Creating IT Solutions
- Setting Up and management of Systems
Computer systems analysts’ employment is expected to expand by 7% between 2019 and 2029, faster than the average for most occupations, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Interface Analyst
The specialty of an interface analyst in pharmacy IT is the smooth integration of various software systems to facilitate communication and data sharing in healthcare settings. Among their duties are:
- Creating and Putting into Practice Interface Solutions
- Ensuring Integrity and Accuracy of Data
- Resolving Interface Problems
The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) found that after implementing optimal interface solutions under the direction of interface analysts, healthcare organizations saw a 30% boost in operational efficiency.
Module Trainer
In pharmacy IT, a module trainer’s main responsibility is to instruct medical practitioners on the features and optimal procedures of certain software modules. Their job descriptions encompass:
- Creating Educational Resources
- Holding Instructional Sessions
- Providing Ongoing Support
90% of pharmacists who participated in a poll conducted by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) said that they felt more competent and confident while utilizing pharmacy IT systems following module training.
Project Manager
In pharmacy IT, a project manager is responsible for managing the development, implementation and completion of technological initiatives in healthcare environments. Their duties involve:
- Outlining the goals and scope of the project
- Taking Care of Resources and Budgets
- Organizing Group Activities
- Ensuring On-Schedule Delivery
Organizations that engage in proven project management techniques save 28 times more money because many of their strategic projects are accomplished effectively, according to research by the Project Management Institute (PMI). Project managers are essential to the effective execution of pharmacy IT initiatives because of their experience.
Enterprise Analyst
Aligning technological solutions with the strategic aims and objectives of healthcare companies is the area of expertise for an enterprise analyst in pharmacy IT. Their main functions are:
- Carrying Out Business Process Evaluation
- Finding Areas That Could Use Improvement
- Recommending IT Approaches or Solutions
- Managing Change with Facilitation
Organizations with strong enterprise analytical strategies have a 20% higher chance of achieving successful digital transformations, according a McKinsey report. By bridging the gap between business requirements and technology capabilities, enterprise analysts ensure that pharmacy IT projects improve patient care while also driving organizational development as well as efficiency.
Consultant
A pharmacy IT consultant provides healthcare businesses with professional advice and help on problems pertaining to technology. What they do entails:
- Evaluating Existing IT Systems
- Offering Suggestions for Enhancement
- Providing Assistance with Strategic Planning
Helping with Integration and Implementation
In a Deloitte survey, 89% of healthcare firms said that using consulting services improved their overall performance and IT strategy. Consultants help healthcare businesses overcome difficult IT problems and accomplish their goals while improving patient care as well as operational efficiency by bringing industry experience along with best practices to the table.
In summary, pharmacy IT specialists bridge the gap between pharmacological knowledge and technology innovation to improve patient care, making them invaluable assets in today’s healthcare environment. Pharmacy IT specialists will play an increasingly more important role as technology develops further.
According to surveys, there is a rising need in this industry for qualified workers as healthcare firms realize how critical IT solutions are to enhance patient outcomes and operational effectiveness. Future developments in pharmacy IT such as telepharmacy, blockchain and artificial intelligence have the potential to completely transform the industry if not present new opportunities for patient care innovation.
Are You Looking to Hire a Proven Pharmacy Rx System Professional?
Helping companies discover the perfect talent for their needs. Finding the right individuals to drive your success is what we excel at.