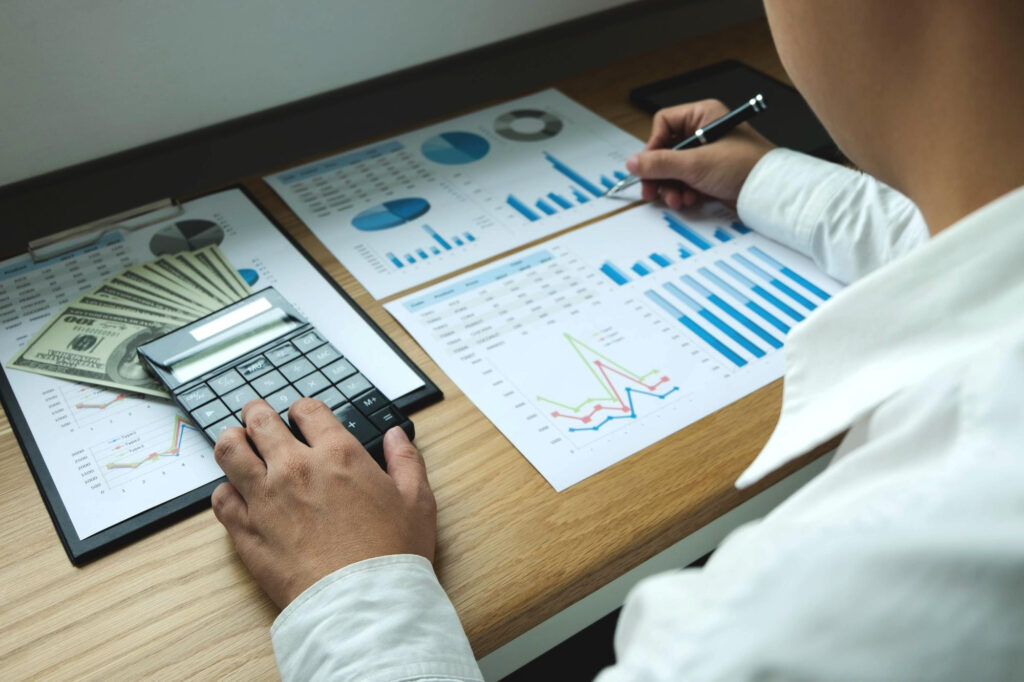
Monitoring the financial well-being and regulatory compliance of international, national as well as local firms, financial controllers are vital resources. They handle internal controls, financial reporting as well as budgets with precision and ethics in today’s company environment. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that from 2019 to 2029, there will be a 15% increase in demand for financial managers, including controllers.
Importance of Financial Controllers in Organizations
Maintaining the trust of stakeholders is largely dependent on financial controllers ensuring accuracy and openness in financial reporting. Additionally, they offer strategic insights that direct executive choices and promote development. According to a Robert Half survey, 88% of CFOs say their financial controllers offer insightful advice on business matters.
Overview of the Article: Addressing FAQs and Providing Salary Insights
In addition to providing compensation trends to empower professionals, this article sheds light on the crucial role that financial controllers play. Financial controllers in the US typically make $92,977 a year (dependent on region and experience), according to Glassdoor. We will explore the duties, requirements and pay scale associated with financial controllers.
What is a Financial Controller?
Definition and Responsibilities of a Financial Controller
A senior-level executive who manages an organization’s finances is known as a financial controller. Internal control protocols, financial reporting and budgeting are all part of their duties. To ensure compliance with regulatory requirements like IFRS (International Financial Reporting requirements) and GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles), they must maintain the transparency and integrity of financial data.
An Association of International Certified Professionals poll found that accountants and financial controllers spend an average of 70% of their time on financial planning as well as analysis, emphasizing the strategic nature of their role.
Key Skills and Qualifications Required
Professionals require a combination of soft skills and technical knowledge to succeed as financial controllers. Important technical qualities include strong analytical skills, precision and financial software expertise. Additionally, working with cross-functional teams and leading strategic projects require strong leadership, problem-solving and communication skills.
Typically, educational requirements include a Bachelor’s Degree in Finance, Accounting or a similar discipline. Advanced degrees can boost reputation and provide opportunities in career advancement. Examples of these degrees include a Master of Business Administration (MBA) or a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) designation.
Importance of the Role in Financial Management
Financial controllers play a pivotal role in organizational finance management by connecting strategic planning with operational execution. Long-term growth is facilitated and executive decision-making is fueled by their analysis as well as precise financial facts. As stated by a Robert Half report, 54% of CFOs consider financial controllers instrumental in driving profitability and efficiency within their organizations.
How Does One Become a Financial Controller?
Educational Background and Qualifications
Prospective financial controllers must have a strong educational background. A Bachelor’s Degree in Accounting, Finance, Economics, or a similar discipline is typically required for employment. A bachelor’s degree is held by 75% of financial managers, including controllers, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
A competitive edge can be gained from advanced degrees like a Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a Finance or Accounting concentration. Candidates with advanced degrees and specialized skills are highly valued by many organizations and can lead to higher level positions.
Professional Certifications and Designations
A major step toward becoming a financial controller is earning professional qualifications. In the accounting and financial fields, the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) designation is highly regarded. CPAs are crucial because they exhibit competence in taxation, auditing and financial reporting to organizations.
Other relevant certifications include the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation, which emphasizes investment management and financial analysis skills as well as the Certified Management Accountant (CMA) certification, focusing on strategic management accounting.
Career Progression Paths to Attain the Role
Acquiring relevant job experience and gradually taking on roles with greater responsibility are common steps in the career path toward a financial controller position. Jobs at the entry level, such financial analyst or staff accountant, offer great experience in budgeting, reporting and financial analysis.
Professionals can progress to positions like senior accountant, accounting manager or finance manager as they gain expertise and prove their abilities. These roles provide chances to supervise financial operations, develop leadership abilities and work with senior leadership.
What Does a Typical Day Look Like for a Financial Controller?
Daily Responsibilities and Tasks:
- Supervising the month-end and year-end closing procedures as well as the financial reporting processes.
- Examining financial data to spot patterns, outliers and areas that could use improvement.
- Tracking financial performance, budgetary compliance and cash flow using important measures.
- Assuring adherence to internal and regulatory standards; working with cross-functional teams to generate financial forecasts and strategic plans.
Balancing Routine Operations with Strategic Initiatives:
- Dividing work between routine tasks like going over financial accounts and big picture projects such as putting process upgrades into action.
- Tasks should be prioritized according to how they affect deadlines and organizational goals.
Challenges Faced and Strategies for Success:
- Taking care of complicated financial matters and balancing competing demands. Managing several deadlines and priorities in a hectic work environment.
- Using technology and automation solutions to improve efficiency and streamline procedures with stakeholders to provide financial insights as well as recommendations.
What Industries Do Financial Controllers Work In?
Overview of Industries Employing Financial Controllers
Financial controllers work in almost every industry, including technology, healthcare, manufacturing and hospitality. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that the manufacturing, banking, insurance, scientific and technical services sectors have the greatest employment rates for financial managers, including controllers.
Varied Responsibilities Based on Industry Specifics
- Financial controllers in the healthcare sector, for instance, can concentrate on controlling revenue cycles, streamlining the reimbursement procedure and ensuring adherence to laws governing healthcare, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
- Financial controllers may work in the technology industry to estimate revenue growth, manage R&D expenditures as well as evaluate the financial sustainability of new product launches.
- In the manufacturing industry, financial controllers may oversee inventory management, cost accounting and supply chain optimization to enhance operational efficiency.
Emerging Trends in Industry-Specific Financial Control
Advancements in technology and changes in regulatory landscapes continue to shape the role of financial controllers across industries. The rise of data analytics and automation tools enables controllers to derive actionable insights from financial data more efficiently. Additionally, industry-specific regulations and compliance requirements necessitate ongoing training and professional development for financial controllers to stay ahead of changes.
Are You Looking to Hire a Proven Financial Controller?
Helping companies discover the perfect talent for their needs. Finding the right individuals to drive your success is what we excel at.
How Does Technology Impact the Role of a Financial Controller?
Role of Financial Software and Automation
The function of financial controllers continues to evolve throughout businesses as a result of technological advancements and changes in regulatory environments. Controllers now more effectively extract relevant insights from financial data, thanks to the development of data analytics and automation solutions. Additionally, financial controllers must continue their professional development and training to stay up to date with industry-specific rules and compliance standards.
- Accounting Software: Financial controllers use a range of software technologies to increase productivity, accuracy and streamline accounting procedures. A Deloitte survey indicates that 76% of financial professionals think automation technologies will have a big influence on their jobs in the next three years. Accounting/receivable/payable procedures, budgeting, and financial reporting are all made easier by platforms like SAP, Xero, and QuickBooks.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: ERP systems combine financial information from many divisions to provide a cohesive picture of organizational performance.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): By automating repetitive processes like data entry and reconciliation, RPA allows financial controllers to concentrate on more strategic endeavors.
Leveraging Data Analytics for Informed Decision-Making
Financial controllers can extract useful insights from massive volumes of financial data with the use of data analytics. PwC conducted a survey and found that 61% of finance leaders think data analytics will significantly influence changes in the finance function.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical financial data, financial controllers can forecast future trends and anticipate potential risks or opportunities.
- Performance Dashboards: Dashboards give controllers instantaneous access to important financial data, allowing them to track performance and make well-informed decisions.
- Advanced Reporting Tools: Financial controllers may generate interactive reports and visualizations with tools like Tableau and Power BI that makes it easier to share financial information with stakeholders.
Future Prospects with Advancements in Technology
It is anticipated that as technology advances, financial controllers’ roles will also change. A McKinsey analysis claims that up to 40% of the work done by financial controllers may be automated with the use of artificial intelligence and advanced analytics.
Financial controllers must embrace technology and keep up with developments if they want to be relevant in a world that is becoming more digitally connected. We’ll go into wage insights for financial controllers in the following section, along with average income ranges by region and variables affecting pay scales.
What are the Salary Insights for Financial Controllers?
Average Salary Ranges by Geographic Location
Geographically, financial controller salaries fluctuate greatly, reflecting variations in the cost of living, talent demand and industry. The typical compensation for financial controllers in the US, according to PayScale, is between $60,000 to over $130,000 per year, with factors such as experience, education, and industry playing a significant role in determining salary levels.
Factors Influencing Salary Levels for Financial Controllers
- Experience: Experienced controllers are paid more, and wage increases are associated with each year of additional experience.
- Education: Higher earning potential might result from professional certifications like the CPA qualification or advanced degrees like an MBA.
- Industry: Industry-specific salaries vary, although financial controllers are generally paid more in industries like finance and healthcare.
- Location: Greater pay is frequently offered to attract talented individuals in urban areas and regions where there is a significant demand for financial talent.
Tips for Negotiating Salary and Advancing in Compensation
- Research: To get a true sense of your value, look into the wage ranges for financial controllers in your area and industry.
- Highlight Achievements: To support your desired wage during salary negotiations, highlight all your achievements and services to the employer.
- Consider Benefits: Think about perks like bonuses, retirement plans and health insurance in addition to base pay when evaluating compensation offers.
- Continued Learning: Invest in ongoing professional development and certifications to enhance your skills as well as increase your value to employers.
What Career Advancement Opportunities Exist for Financial Controllers?
Transitioning to CFO or Executive Leadership Roles
A common goal for financial controllers is to become an executive leader, such as a chief financial officer (CFO). In their capacity as CFOs, they strategically influence corporate strategy, oversee financial risk and spearhead expansion projects. A Robert Half poll found that 45% of CFOs began their careers as controllers, underscoring the possibility of professional advancement inside the finance function.
Entrepreneurial Ventures and Consulting Opportunities
Financial controllers are highly skilled in both finance and strategy, which makes them valuable in non-traditional business environments. Some decide to take advantage of their experience to start their own firms or offer financial advising to companies. Controllers seeking to design their own course might find flexibility and autonomy in the entrepreneurial road, whether it’s founding a boutique consulting firm or offering startups financial strategy advice.
Non-Traditional Career Paths and Specializations
Financial controllers have the opportunity to pursue unconventional career paths and specialized responsibilities that align with their interests and areas of competence, outside of the corporate finance domain. There are opportunities in non-profit organizations, government, academia and forensic accounting. Specializations in international finance, risk management, mergers and acquisitions provide opportunities to pursue fulfilling career paths as well as improve knowledge base.
What Skills Are Most Valuable for Financial Controllers?
Technical Accounting Skills
- Financial Reporting: A thorough understanding of financial reporting standards, such as IFRS or GAAP, is necessary to prepare accurate and compliant financial statements.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Controllers that are proficient in forecasting and budgeting may create detailed financial plans and provide strategic direction for decision-making.
- Internal Controls: Financial information is reliable and accurate when internal control processes and risk management concepts are understood.
- Taxation: Controllers can optimize tax strategies and ensure tax compliance by having a thorough understanding of tax rules and regulations.
Analytical and Problem-Solving Abilities
- Data Analysis: Controllers that possess strong analytical abilities are able to decipher financial data, spot trends and gather useful insights that improve company performance.
- Critical Thinking: Controllers benefit from having the critical thinking skills necessary to assess financial data and make sensible decisions in complex circumstances.
- Problem-Solving: Controllers have to be skilled in seeing problems with money and coming up with innovative ways to solve them, such as cutting expenses or improving cash flow.
Soft Skills such as Communication and Leadership
- Communication: To effectively communicate financial insights to stakeholders, including CEOs, board members and team members, financial controllers must possess strong communication skills.
- Leadership: To inspire and encourage their teams, promote teamwork and advance company goals, controllers need to be highly capable leaders.
- Adaptability: Controllers must be able to adjust to shifting business conditions, technological advancements and legal requirements to succeed in fast-paced companies.
Searching for Skilled Financial Controllers? Contact The THOR Group Today!
Drive growth and unlock new opportunities with expert Financial Controllers. Specializing in financial management, these professionals may help streamline processes, optimize financial reporting, and enhance fiscal strategies. If your company needs experienced Financial Controllers, The THOR Group can provide the expertise to elevate your organization.
Partner with The THOR Group, a reliable ally for businesses looking to excel in financial management. These Financial Controllers are available for consulting, contracting, or direct hire basis. Contact us today to maximize your company’s financial potential!
Are You Looking to Hire a Proven Financial Controller?
Helping companies discover the perfect talent for their needs. Finding the right individuals to drive your success is what we excel at.